Dr. Terencia. A, Dr. C Jayakumar, AIMS KOCHI
2 months Old term, male Small for gestational age presented with multiple episodes dysentery low grade intermittent fever and poor activity and failure to thrive since 42 days of life. Child had raised inflammatory markers, CSF evidence of meningitis at admission . USG showed multiple splenic abscesses.Child bilateral coarse crepitations and Hepatosplenomegaly.
Differentials considered were-
1. Intra-uterine infections
2. Immunodefeciency
3. Early onset IBD
4. Metabolic disorders
5. Urosepsis
Chest x-ray(Figure 1) done showed bilateral patchy opacities(?fungal balls).

USG abdomen(Figure 2) showed multiple splenic abscesses.

CECT Chest(Figure 3)-Multiple nodular parenchymal densities , suggesting an infective etiology. Possibilities include disseminated TB, fungal or other atypical infections
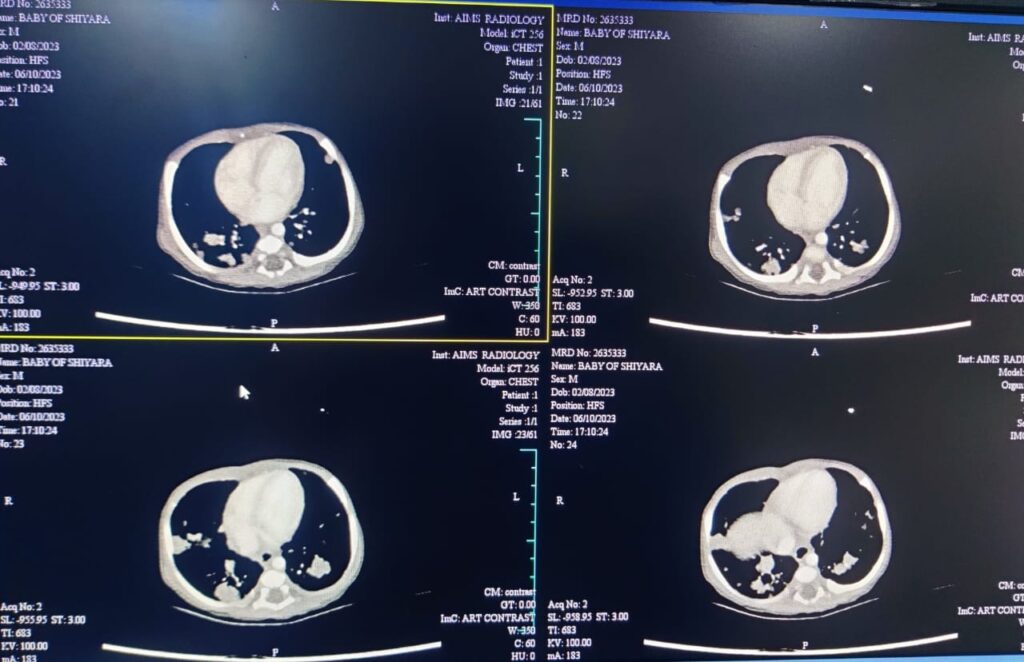
Child was started on IV antibiotics (vancomycin &Ciprofloxacin )and other supportives. CECT chest showed Multiple nodular parenchymal densities , suggesting an infective etiology. CMV IgM was positive and CMV quantification done showed 84.3 copies. Repeat CMV copies were negative. Blood culture showed significant growth of burkholdaruiasepsis and antibiotics were changed as per sensitivity to Cetazidime and septran. Galactomanan assay sent was negative.
His fever spikes gradually settled. In view of these recurrent infections possibility of primary immunodeficiency was considered.
Flow cytometry of Basic Lymphocyte Panel–
The scatter parameters and the antigen expression profile as studied flow cytometry of the sample shows increase in WBC count, Absolute Lymphocyte count, Absolute CD3+ T lymphocyte count, Absolute CD4+ T lymphocyte count, Absolute CD8+ T lymphocyte count, Absolute CD19+ B lymphocyte count and Absolute NK CD56+/ CD16+ cell count as per the age-wise reference values.
Immunoglobulin profile-
IgG-752 (227.0 – 1378.0 ( mg/dl ))
IgM-120.7 (0.0 – 121.0 ( mg/dl ))
IgA-36.8 (0.0 – 81.0 ( mg/dl ))
IgE-22.710 (0.0 – 15.0 ( IU/ml ))
NBT DHR showed Neutrophil oxidative burst appears absent suggestive of Chronic Granulomatous Disease(CGD).
Child was managed IV antibiotics, antifungal nebulised bronchodilators and other supportive measures. In view of poor weight gain nasogastric tube was inserted and he was started lactose free formula feeds and MCT oil. The present condition of the child, diagnosis ,complication,treatment option including BMT were explained in detail to the parents. HLA typing of parents were done and both were haplo match. Donor HLA Specific Antibodiesagainst father is negative. As parents wants to continue further treatment in other hospital he was discharged at request. Child is awaiting BMTcurrently.
Points favouring immunodeficiency leading to diagnosis of CGD were SGA ba with hepatosplenomegaly, failure to thrive , multiple splenic abscesses, recurrent infections and Sepsis.
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a rare heterogeneous condition described as a series of recurrent life-threatening infections. Defective phagocyte NADPH oxidase causes the disease. The ultimate result is the inability of phagocytes such as neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages to destroy certain microbes. Hence are highly susceptible to frequent and sometimes life threatening bacterial and fungal infections. CGD is diagnosed special blood tests that show how well phagocytes produce hydrogen peroxide, an indicator that they are functioning properly. Children will need lifelong regimens of antibiotics and anti-fungals to prevent infections.
Definitive treatment of CGD-
Bone marrow transplantation, however not without significant risk.
Fate of CGD-
The average patient now survives at least 40 years due to large part to routine lifelong use of prophylactic anti-microbial agents. Survival is better in AR forms more than X-linked forms. Protocols for hematopoietic cell transplantation(HCT) are improving and offering promise with definitive correction. Gene therapy approaches are under development and may eventually replace HCT. Until then HCT is the recommended curative approach for those with available donors.
