Dr Anakha V Ajay
Dr Sajith Kesavan (intensivist and Paed pulmonologist )Dr Greeshma Issac(intensivist ) Dr C Jayakumar(Dept of paediatrics) AIMS Kochi.
One year old female3rd child of non consanguineous parentage term, AGA with normal natal history presented with stridor for one month duration
Evaluation at an outside with CT chest was suggestive of-compromise of cervical tracheal lumen with ?septum ? endobronchial filling defect due to foreign body.
Child had history of multiple hospital admission for the last one month in view of persisting stridor
. Child is developmentally normal till age and immunised uptodate
At admission child tachypneic with suprasternal and subcostal retractions with stridor present and other stable vitals.and normal PICCLE
RESP system examination normal vescicular breath sounds heard with conducted sounds.
Differentials
Thymopharyngeal remnant lesions with ? neoplastic transformation
Germ cell tumors
Lymphoma.
Labs TC- 9.8ku/ml N-52.3% L-35.2% PLT-437ku/ml HB-9.5g/ml CRP- 4.01mg
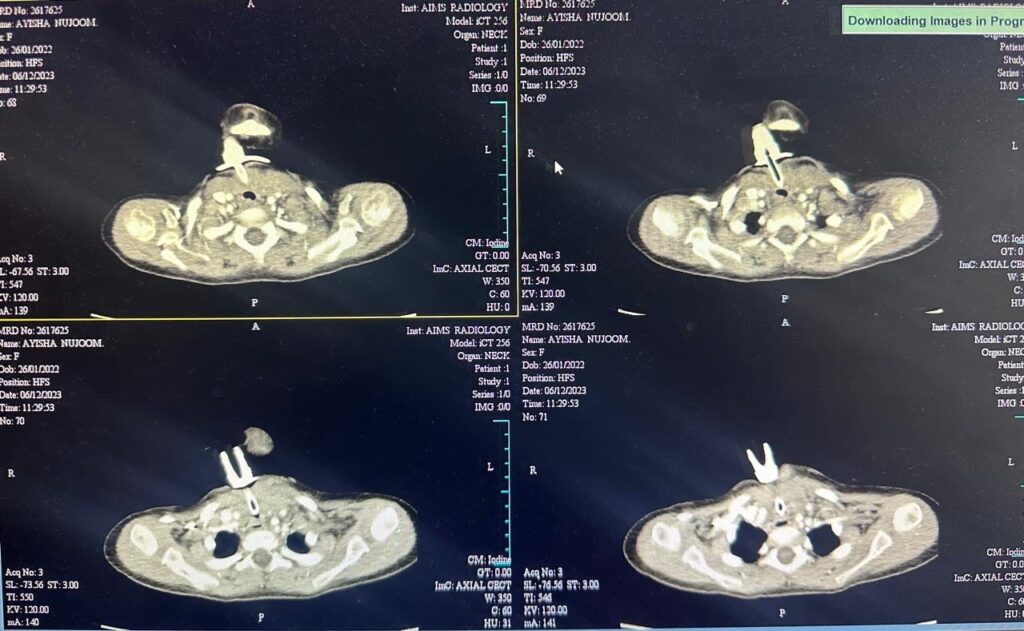
CECT Chest revealed soft tissue lesion in lower neck , midline with minimal extension into the anterior superior mediastinum causing marked tracheal compression and narrowing.
After the CECT surgical excision done under GA with intraoperative findings of hard whitish mass present in the midline, lying over the trachea, infiltrating thyroid gland on either side compressing the anterior wall of trachea.
Histopathology neoplasm composed of broad sweeping fascicles of spindle cells.The cells are spindly with pale vesicular ovoid elongated nuclei, conspicuous nucleoli and moderate cytoplasm.They are wavy in appearance. Sprinkling of lymphocytes, microhaemorrhages and extravasated,RBCs noted. Collagenous stroma noted. Focally lesion is seen infiltrating surrounding soft tissue andlymph nodes seen show reactive changes.
No evidence of atypia / mitosis/necrosis noted.
IHC : Cells show patchy positivity for smooth muscle actin(SMA),desmin and beta-catenin. S100 ,CD34,h-caldesmon and myoD1 are negative.Ki67 index is 2-4%.
Features are suggestive of fibromatosis.
Child was noticed to have stridor post extubation.
Hence Bronchoscopy was done which revealed bilateral vocal cord palsy , cords in adducted position, there was only inward movement paradoxically during inspiration and moderate tracheomalacia in mid trachea.
Child was incidentally detected to have trachea leak between 3-4th tracheal ring and was repaired and tracheostomy done on day 12 of admission.
In view of ? aspiration, VFSS was done and was advised to continue only thick liquids and semi solid and to consider alternate mode of feeding for thin liquids.
Hence ,plan to insert NG tube prior to discharge and to give thin liquids through the NG tube.
Semisolid feeds and thick liquids were addicted as power the parental wish
Patient was readmitted after 3 months with complaints of mass over cervical region.
CT chest showing Minimally enhancing residual lesion between the medial ends of clavicle in the suprasternal notch, minimally superior mediastinal extension. disease is extensive and abutting right brachiocephalic and trachea. Case after discussing with GI surgery and medical oncology was opined as surgical excision cannot be considered at present and in view of recurrence and growth , to try medical treatment.
Plan was to start tamoxifen (Tab. Tamoxifen 5mg OD). Prognosis has been explained to the parents. Child is planned to be kept under regular follow up
CT SCAN SHOWING CERVICAL FIBROMATOSIS
Fibromatosis is a histologically benign, most common fibrous neoplasm that arise from the musculoaponeurotic tissues of the body. It is slow growing and locally infiltrative disease.
There are two forms of disease- a solitary form and a disseminated form with multiple lesions.
It can have significant morbidity when it occurs in the head and neck region because of proximity to vital structures.
Despite having benign histology being locally aggressive it can cause significant morbidity.
Diagnois is usualy imaging and confirmation is histopathology.
Fibromatosis is best managed multidisciplinary approach.The disesase is usually partially resectable when presented below deep cervical fascia. Post operative radiation along with tamoxifen therapy offers good results when complete excision is not possible due to involvement of neurovascular structures.Follow up has to be manintained in all cases as there are high chances of recurrence especially in the first 2 years. Recurrence risk is higher for younger patients.
Prognosis-
Varies according to the type and localization.Forms without visceral involvement have an excellent prognosis with a spontaneous regression of the lesions in 1-2 years.
Generally the prognosis of solitary musculoskeletal fibromatosis is favourable with persistant risk of recurrence.
Take home message- Early detection and interdisciplinary management are crucial in addressing the complexities of cervical fibromatosis, emphasizing the importance of tailored treatment plans and long term surveillance for optimal patient outcomes.
