Dr. Venumadhav, Dr.sheela (Paed Genetics) Dr. C. Jayakumar
Department of Pediatrics, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences
A six-year-old male, the first child of non-consanguineous parents, presented to the outpatient department with a history of involuntary shock-like jerks, which were notably absent during sleep. The parents also reported the presence of abnormal swellings over the bony prominences for the past 1-2 years. The child had normal development up to the age of two, except for a mild speech delay. However, post this period, teachers observed a decline in his communication skills, increased inattention, and difficulty engaging in play activities, leading to a label of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and initiation of therapies. Additionally, the parents noted increased behavioral issues, including hyperactivity and paroxysmal events, prompting further evaluation.
Examination and Investigations:
On examination, the child was irritable and inattentive. He exhibited dysmorphic features. A head-to-toe examination revealed subcutaneous nodules over the bony prominences of his hands and legs. Systemic examination indicated hepatomegaly and mild appendicular hypotonia.
Labs Microcytic hypochromic anemia with a HB 10.8 g/dL and a platelet count of 270 x 10^9/L

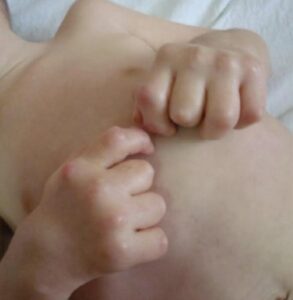
Above pictures showing subcutaneous nodules
Differential Diagnosis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis:
Tuberous sclerosis complex
Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
MEN2b
Niemann pick disease
Lysosomal storage disorders
Prolonged VEEG done showed generalised epileptiform abnormalities.
In view of clinical features, EEG and examination findings, genetic consultation was availed.
WES was done , suggestive of Compound heterozygous, autosomal recessive mutation (Father- 1 LP, Mother –vus)
Acid ceramadise levels were done and found to be low
Echocardiogram (Echo), visual evoked potentials (VEP), brainstem auditory evoked response (BERA), and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) were all normal.
Fundus examination revealed a normal disc with healthy pink macula.
Farber’s disease was diagnosed based on clinical, genetic, and biochemical findings:
• Clinical features include subcutaneous nodules, hepatomegaly, neurological symptoms, and developmental delay.
• Genetic confirmation with WES showing compound heterozygous mutations.
• Biochemical confirmation with low acid ceramidase levels.
Treatment and outcome
He was initiated on a regimen of two antiseizure medications to manage the epileptiform abnormalities observed on the VEEG.
However, enzyme replacement therapies, a common treatment approach for many lysosomal storage disorders, are presently unavailable
Given the child’s relatively stable condition for his age, a bone marrow transplant was planned as an outpatient procedure.
This therapeutic strategy aims to provide normal enzyme-producing cells, potentially halting or even reversing the progression of Farber’s disease. Regular follow-up and monitoring will be essential to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and ensure the child’s well-being.
DISCUSSION:
Farber’s disease is a very rare lysosomal storage disorder characterized a deficiency of acid ceramidase enzyme, leading to the accumulation of ceramide in tissues. Clinical manifestations include subcutaneous nodules, joint stiffness, hepatosplenomegaly, and neurological symptoms such as seizures and developmental delay. Diagnosis involves genetic testing to identify compound heterozygous mutations and biochemical analysis to confirm low acid ceramidase levels. Enzyme replacement therapies are currently unavailable, and treatment options focus on symptomatic management, including antiseizure medications. Bone marrow transplant may be considered in select cases to potentially halt disease progression. Regular monitoring and supportive care are essential to manage the multisystemic manifestations of Farber’s disease.
