Dr Adeena D S, Dr.Sheela Namboothiri , Dr Praveena, Dr.Navya George , Dr C Jayakumar
Amrita institute of medical sciences
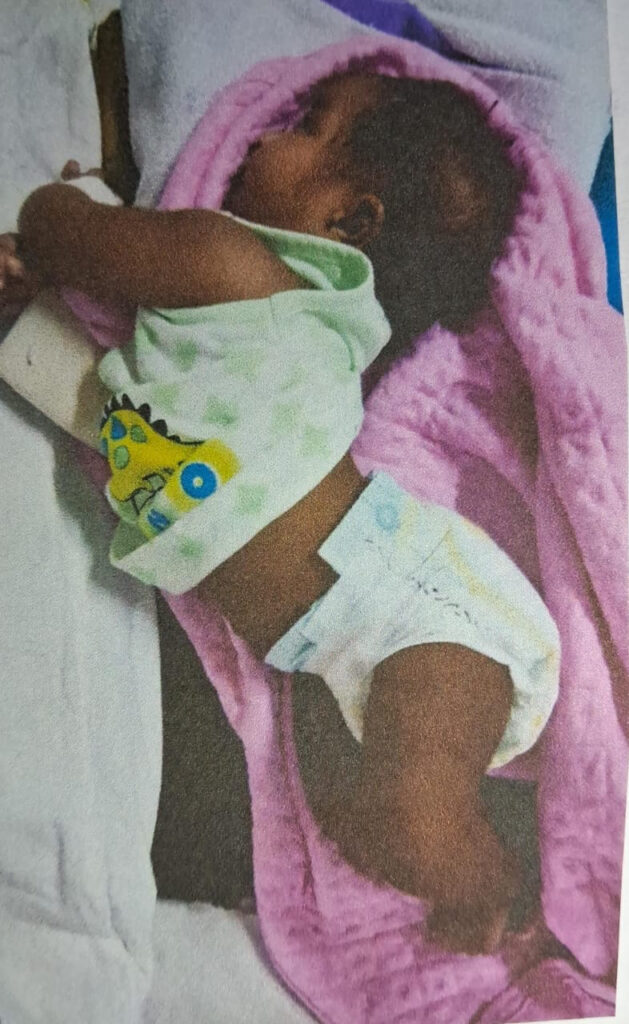
Three month old female child 2nd born of a non consanguineous parentage at 36th week to a mother with glaucoma on medications in pregnancy presented with the complaints of frequent arching of back and abnormal sound of cry noticed since birth,
She had a visible neck swelling during crying for the past 2 weeks.
H/o polyhydraminos at 8th month of gestation. Postnatally child had poor sucking, lethargy and h/o 2-3 hypoglycemic episodes and cyanosis requiring NICU stay for 6 days.
Development social smile nil
Family history of glaucoma in maternal family.
O/e -Alert ba ,eye contact+, microcephaly,
Dysmorphicroundface,hypertelorism,
bilateral epicanthic fold,bilateral convergent squint,tiny toe nail
Midline neck swelling protruding during crying
Abnormal high pitched cat-like cry
Occasional ophisthontonic posturing
Wt-4.23 kg,length-55 cm,HC -36 cm-all parameters below 3rd centile
CNS-cranial nerves normal, mild hypertonia, brisk DTR.
Other systems within normal limits.
Investigation showed normal counts. Ultrasound neck showed cervical protrusion of an otherwise normal thymus. Bronchoscopy done in view of abnormal cry showed a pulsatile midline swelling ,short vocal cords and mild -moderate tracheomalacia, with a high suspicion of Cri-du-chat syndrome.
High resolution karyotype sent showed apparently abnormal female chromosome complement in all cells examined with a terminal deletion of distal short arm of chromosome 5-deletion consistent with diagnosis of Cri-du-Chat syndrome.
dysmorphism
Discussion-Cri du Chat syndrome-Cri du chat syndrome is a genetic disorder caused a deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5. The name of the syndrome means the cry of the cat and describes the main clinical finding of a high-pitched, monochromatic cat-like cry. The clinical picture, severity, and progression of the disease vary depending on the region of the chromosome that is deleted. This disorder is often characterized distinctive facial features, delayed development, and intellectual disability.
In the neonatal period, the most characteristic finding is a high-pitched, monotonous cry, which usually disappears within the first few months of life. Other associations-low birthweight, microcephaly, asphyxia, muscle hypotonia, and impaired suction. Craniofacial Malformations- microcephaly, moon face, hypertelorism, prominent epicanthic folds, large nasal bridge, short philtrum
If clinical suspicion is high, a karyotype analysis can confirm the diagnosis. In the presence of a normal karyotype, more specific cytogenetic studies such as FISH or CGH can be carried out. Complications include heart defects, hearing or visual difficulties, intellectual disabilities.
The occurrence of specific characteristic findings such as microcephaly, low birth weight, moon face, muscle hypotonia, and a cat-like cry together should raise clinical suspicion of the condition. Sometimes, this can be difficult because the features may not be obvious as patients show a cytogenetic variation leading to phenotypic variation.
Most cases result from a sporadic denovo deletion that is associated with a low recurrence risk. If either parent has a balanced translocation,the recurrence risk will be 5-15%, depending on parental origin.
Take home message
All dystrophic children may be evaluated with a view to give the best possible care and to prevent subsequent recurrence in the family