Dr. Rithwik Sunil, Dr Vinitha Prasad, Dr C Jayakumar
AIMS KOCHI
Twelve year old presented girl with alleged h/o consumption of a yellow fruit on 21/08/24 at 5:30 pm. After chewing the fruit, she found the taste bitter and immediately spat it out. The teacher was informed and the child’s parents were acknowledged
Past History
No h/o previous poisoning
All other pediatric history were normal
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
◼ Child is afebrile, alert and conscious
◼ Vitals-
• Temp:98.2F,
• PR-84/min, RR:15/min,
• BP:101/57mmhg,
• Spo2:100% in RA
◼ No pallor,icterus,clubbing,cyanosis,lymphadenopathyor edema
Systemic Examination
◼ CVS-S1S2+, no murmurs
◼ RS- AEBE, NVBS, no added sounds
◼ CNS- NFND
◼ P/A- soft, non-tender, no organomegaly
◼ Musculoskeletal-Normal ROM
Labs
Tc:16.91
Hb: 13.5
Neutrophils :74%
Lymphocytes:19%
Platelets:368
LFT: Normal
RFT: Normal
Na:143mEq/l K:3.3mEq/L
CRP (C-reactive protein) : 1.68 mg/LCK MB : 2.51 ng/mlPhosphorus inorganic (phosphate)Serum : 5.0 mg/dl
Hs Trop T : 0.0040 ng/mlCreatine kinase (CK), Total-Serum : 160.0 U/L
Magnesium : 2.0 mg/dl
Calcium; total – Serum : 9.65 mg/dl
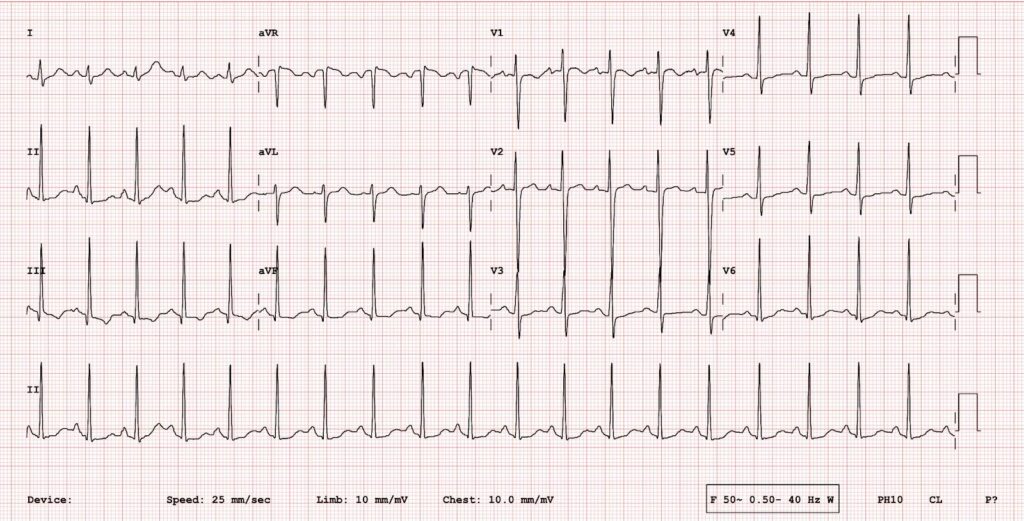
ECG (21/8/24) – sinus rhythm , QTc prolonged- 440msec
Differentials considered
◼ Unsupervised ingestion of medications
◼ Oleander
◼ Datura
◼ Organophosphate poisoning
Course in the hospital
◼ Vitals were stable. There was no arrythmia. Systemic examination was within normal limits. Counts/ LFT/RFT were normal. Potassium was 3.3mmol/L for which correction was given. Cardiac markers were within normal limits.
ECG was taken which showed QTc prolongation (400msec) and did not reveal any heart block.
Cardiac evaluation with ECHO was normal. Child was monitored for 36 hours. Repeat ECG and electrolytes were within normal limits.
Oleander Poisoning
The two types of oleander are commonly encountered in India ,pink oleander and yellow oleander. Both are predominantly cardiotoxic. Most such cardiotoxic plants contain various cardiac glycosides which act in similar fashion.
The usual fatal dose comprises 15–20 g of root or 8–10 seeds. In general, yellow oleander is more toxic than pink oleander.
Clinically
Gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations are followed cardiovascular features such as marked bradycardia with PR and QRS prolongation. Sinus arrest, varying degrees of atrioventricular (AV) block with dissociation, or escape rhythms may occur, including paroxysmal atrial tachycardia with AV block, junctional tachycardia. Hyperkalemia is common
Children (less than 12 years old): in case of evidence of ECG changes, with continuous cardiac monitoring, slowly give 0.1 mL/kg body weight (max. 10 mL) 10% calcium chloride.
Give nebulized salbutamol (2.5 mg if younger than 2.5 years; 5 mg if 2.5–7.5 years; 10 mg if older than 7.5 years) and remeasure serum potassium and blood pH.
Digoxin-specific antibodies (digoxin-specific Fab fragments) are the treatment of choice for severe bradyarrhythmias with hypotension unresponsive to atropine and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
Take home message
All the parts of this plant, especially the seeds and root are poisonous. It is essential to know and identify the plant and act in haste

