Dr Anakha V Ajay , Dr Aswin Prabhakaran (Deptof Pediatric surgery) Dr Jayasree Dr Perraju Dr Smrithi Dr Ashwin Dr Lakshmi (Dept of Neonatology) Dr C Jayakumar(Dept of Pediatrics) AIMS Kochi
Four day old out born ba born to a 27 year old gravida 3 para 2 living 2 mother at 39+6 weeks of gestation normal vaginal delivery. Pregnancy was uneventful and no foetal anomalies were detected at prenatal ultrasound. Ba cried immediately after birth with Apgar score of 9 at 1min and 5 min. Ba presented at birth with a genitourinary midline infra umbilical wall defect with visible urinary bladder and associated malformation of penis and bilateral undescended testes. Hence ba was referred to our institute under paediatric surgery for surgical correction.
At admission ba was alert and active with stable vitals.
Auxology: Weight- 2.88 kg HC- 34 cm L- 48 cm On examination: Midline infraumbilical defect with extrophy of bladder and dysplastic penis was noted. No other obvious external anomalies present. Systemic examination were within normal limits. Hips and spine were normal.
Ba was received in NICU and was on room air since admission. Ba was hemodynamically stable without any inotropic support and started on full feeds. Cerebral, cardiac and abdominal ultrasound were then performed turning out to be normal.
Kidney ultrasound showed trace left collecting system prominence.(APD-3mm).
Ba was intubated and taken up for Bladder exstrophy repair with osteotomy. Posterior osteotomy done. Bladder plate mobilized and closed in a horizontal fashion. Pubic bones approximated. Rectus closed in the midline. Skin closed with ureteric and urethral catheters in situ, brought out through bladder opening
Post operatively two urethral catheters, one transurethral catheter and an epicystostomy tube were left indwelling. In the first 3 weeks the patient was kept immobilised with pelvis and lower limbs wrapped around and suspended in a special hammock device(modified Bryant traction).Parenteral nutrition was administered during this period. Full enteral feeding was restored at day 10 postoperatively.
Tubes were sequentially removed during the fourth postoperative week and ba was discharged on post operative day 28. Further plan is urethral reconstruction 1 year of age and bladder neck reconstruction 4 years.
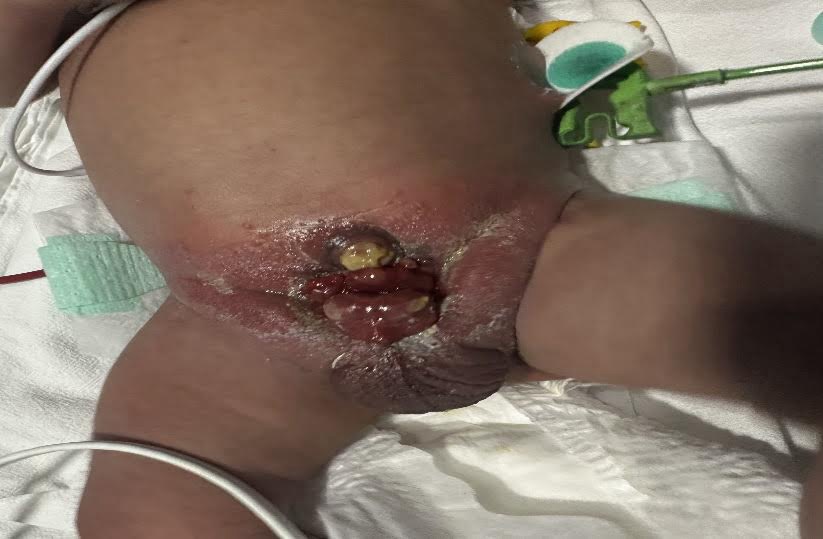
Extrophy of Bladder
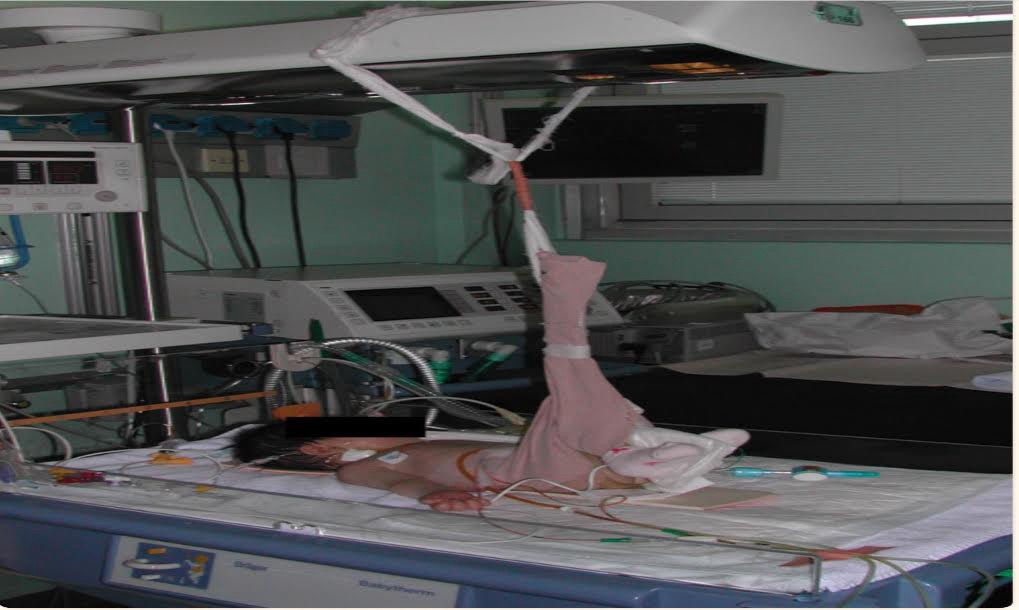
Modified Bryants Traction
Extrophy of bladder is a rare condition with incidence of 1 per 30,000-50,000 live births with male to female ratio ranging from 1.5:1 to 5:1. The condition is thought to be caused incomplete development of the infraumbilical part of the anterior abdominal wall, associated with incomplete development of the anterior wall of the bladder owing to delayed rupture of the cloacal memberane.Diagnosis can be made antenatal ultrasound. In neonates extrophy of bladder is diagnosed on clinical examination, workup includes baseline RFT, before complex reconstruction of the urinary tract. Renal USG to rule out renal anomalies and urinary tract dilatation. The goals of surgery are to close the bony pelvic ring close the bladder posterior urethra and close the anterior abdominal wall defect and reconstruct the genetalia. In the first year of life, the bladder is closed following osteotomy of both iliac bones. Later reconstruction of bladder neck and sphincter is done.
Prognosis: Most babies have good long term outcomes if they have surgery to treat bladder extrophy.
Take home message: To highlight the importance of early diagnosis and comprehensive management in improving patient outcome.
